[삼성SW역량테스트] 청소년 상어::알고리즘
2020. 6. 29. 17:28ㆍalgorithm/bfs
2020 상반기 삼성전자 SW 역량테스트 문제
출처 : BOJ(https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/19236)
4 x 4 공간 안에 물고기 16마리가 존재하고, 상어가 (0, 0) 지점의 물고기부터 먹기 시작해 먹은 물고기 방향으로 나아가며 먹기를 반복하는 문제입니다.
BFS로 4 x 4 공간인 map과 물고기의 정보를 단계마다 저장할 수 있도록 HashMap과 Key인 cnt를 활용해 문제를 풀었습니다. 사이클마다 계속해서 map이 변하고, 물고기의 이동 방향이 변하기 때문에 HsahMap에 저장하는 방법을 선택했습니다.
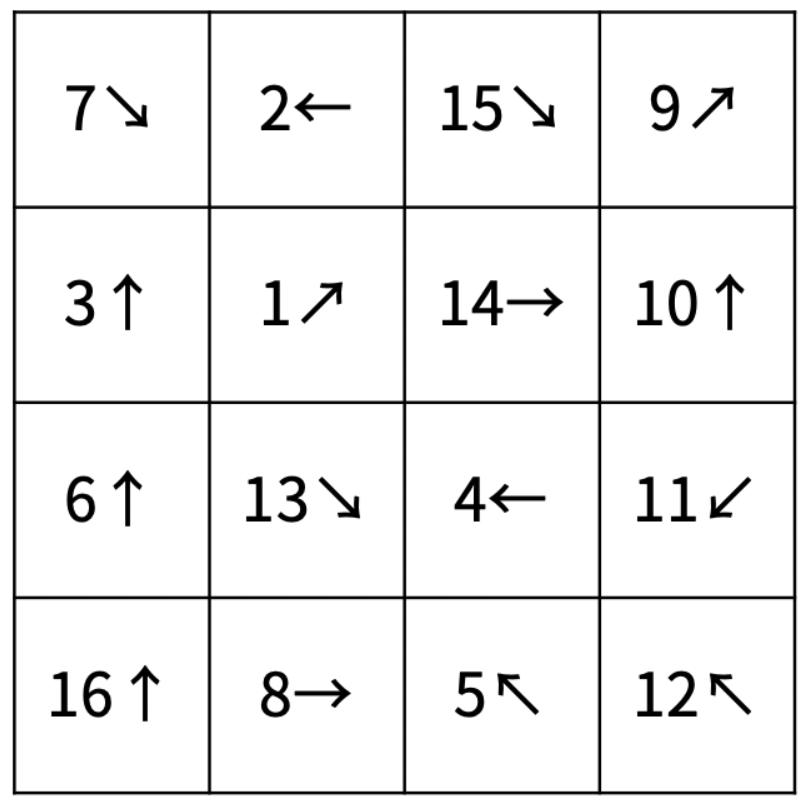


우선, 상어가 (0, 0) 자리에 들어오고, (0, 0) 자리에 있던 물고기의 번호(num)를 섭취하고, 방향(d)을 가지게 됩니다.
이후 그 방향에 있는 모든 물고기의 번호를 섭취하고, 방향을 가질 수 있습니다.
물고기가 없는 빈 공간(0)은 갈 수 없습니다.
모든 루트에서 상어가 가진 방향으로 가다가 4 x 4 공간 밖으로 나가게 되면 끝이 나고, 최대값을 구합니다.
Java 코드
package bfs;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_19236_청소년상어 {
public static int answer, cnt; // 최대값, queue에 따른 정보를 저장하기 위한 변수
public static Map<Integer, int[][]> sMap; // queue에 따른 map 정보 저장
public static Map<Integer, Map<Integer, int[]>> fMove; // queue에 따른 fish 정보 저장
public static Queue<int[]> q; // bfs 구현을 위한 queue
public static int[][] dir = {
{0, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1},
{0, -1}, { 1, -1}, { 1, 0},
{1, 1}, { 0, 1}, {-1, 1}
};
public static void bfs() {
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] s = q.poll();
int[][] map = sMap.get(s[4]); // cnt를 이용해 queue에 따른 map 정보 불러오기
Map<Integer, int[]> f = fMove.get(s[4]); // cnt를 이용해 queue에 따른 fish 정보 불러오기
int sum = s[3] + map[s[0]][s[1]]; // 물고기 번호 섭취
answer = answer < sum ? sum : answer; // 최대값 확인
map[s[0]][s[1]] = -1; // 상어 위치 표시
move(map, f); // 물고기의 이동
map[s[0]][s[1]] = 0; // 상어가 물고기를 먹고 난 후 빈 자리 표시
// 상어의 이동
int y = s[0] + dir[s[2]][0];
int x = s[1] + dir[s[2]][1];
// 상어가 가진 방향에서 먹을 수 있는 물고기를 모두 queue에 대입
while (0 <= y && y < 4 && 0 <= x && x < 4) {
if (map[y][x] != 0) {
// map과 fish 정보는 주소값으로 저장되기 때문에 새로운 배열과 HashMap을 만들고 새로운 주소로 저장
int[][] cMap = new int[4][4];
Map<Integer, int[]> cFish = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
cMap[i][j] = map[i][j];
}
}
cFish.putAll(f);
sMap.put(cnt, cMap);
fMove.put(cnt, cFish);
q.offer(new int[] {y, x, f.get(map[y][x])[2], sum, cnt++});
}
y += dir[s[2]][0];
x += dir[s[2]][1];
}
}
}
// 죽은 물고기인지 확인
public static boolean dead(int[][] map, int num) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
if (map[i][j] == num)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void move(int[][] map, Map<Integer, int[]> f) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 16; ++i) {
if (dead(map, i))
continue;
int[] l = new int[] {f.get(i)[0], f.get(i)[1]};
int d = f.get(i)[2];
int y = l[0] + dir[d][0];
int x = l[1] + dir[d][1];
// 방향을 먼저 잡음
while (y < 0 || 4 <= y || x < 0 || 4 <= x || map[y][x] == -1) {
d = (d + 1) % 9;
if (d == 0) d = 1;
y = l[0] + dir[d][0];
x = l[1] + dir[d][1];
}
// 해당 방향으로 한 칸 이동
// 만약 해당 칸에 물고기가 없다면 0과 swap, 있다면 그 물고기와 swap
if (map[y][x] == 0) {
map[l[0]][l[1]] = 0;
}
else {
f.put(map[y][x], new int[] {l[0], l[1], f.get(map[y][x])[2]});
map[l[0]][l[1]] = map[y][x];
}
f.put(i, new int[] {y, x, d});
map[y][x] = i;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
answer = 0;
cnt = 0;
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[][] map = new int[4][4];
Map<Integer, int[]> f = new HashMap<>();
sMap = new HashMap<>();
fMove = new HashMap<>();
q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine().trim());
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
f.put(map[i][j], new int[] {i, j, Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken())});
}
}
sMap.put(cnt, map);
fMove.put(cnt, f);
q.offer(new int[] {0, 0, f.get(map[0][0])[2], 0, cnt++});
bfs();
System.out.println(answer);
}
}